导航栏 安装插件
新建NavBar.vue组件,使用vueinit自动提示命令初始化一个vue页面。scoped的意思是在当前组件中的样式是独立的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 <template> <div> </div> </template> <script> export default { } </script> <style scoped> </style>
Bootstrap使用 https://v5.bootcss.com/
快速入门https://v5.bootcss.com/docs/getting-started/introduction/
寻找合适的导航栏
创建NavBar 通常把关于具体页面的组件,创建在src\views文件夹下,把涉及到的公共组件,放入src\components中
对于导航栏,创建src\components\NavBar.vue
将Bootstrap找到的代码粘贴到<template>中,
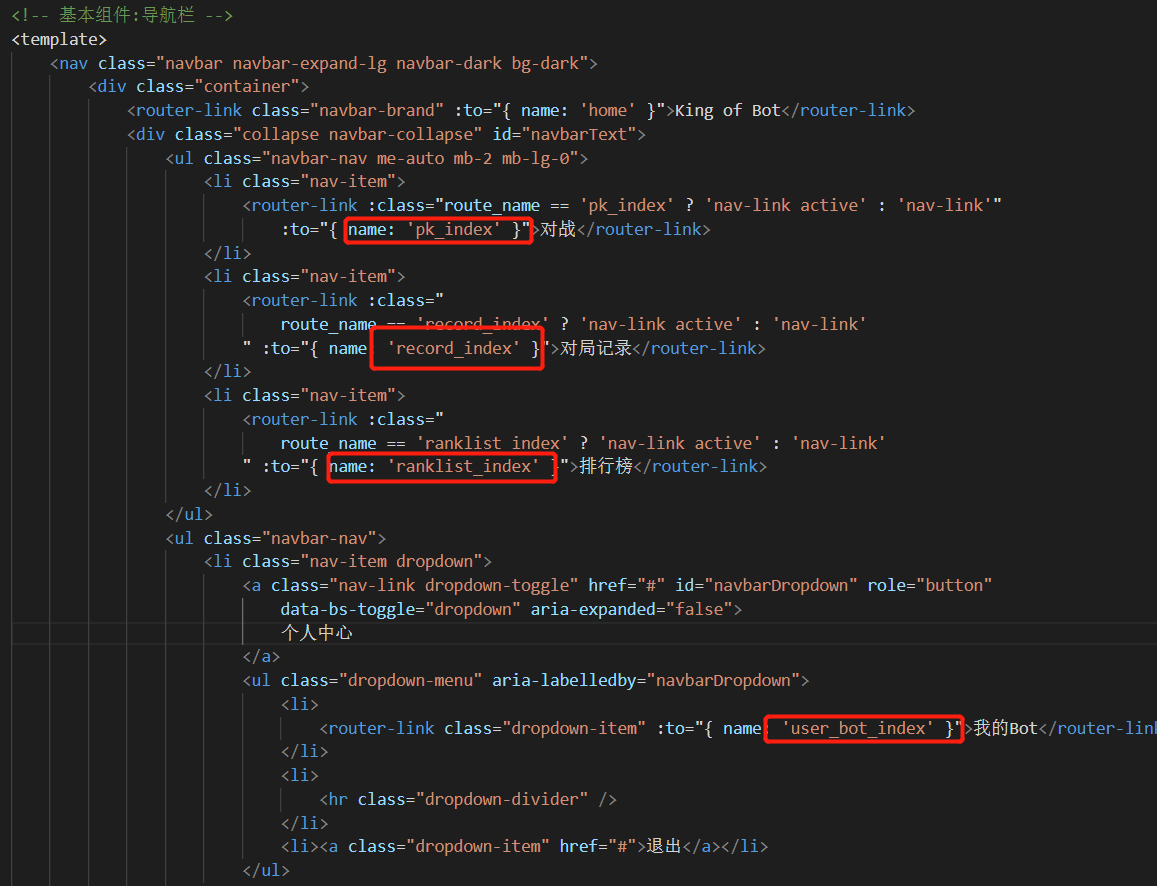
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 <template > <nav class ="navbar navbar-expand-lg navbar-dark bg-dark" > <div class ="container" > <router-link class ="navbar-brand" :to ="{ name: 'home' }" > King of Bot</router-link > <div class ="collapse navbar-collapse" id ="navbarText" > <ul class ="navbar-nav me-auto mb-2 mb-lg-0" > <li class ="nav-item" > <router-link :class ="route_name == 'pk_index' ? 'nav-link active' : 'nav-link'" :to ="{ name: 'pk_index' }" > 对战</router-link > </li > <li class ="nav-item" > <router-link :class =" route_name == 'record_index' ? 'nav-link active' : 'nav-link' " :to ="{ name: 'record_index' }" > 对局记录</router-link > </li > <li class ="nav-item" > <router-link :class =" route_name == 'ranklist_index' ? 'nav-link active' : 'nav-link' " :to ="{ name: 'ranklist_index' }" > 排行榜</router-link > </li > </ul > <ul class ="navbar-nav" > <li class ="nav-item dropdown" > <a class ="nav-link dropdown-toggle" href ="#" id ="navbarDropdown" role ="button" data-bs-toggle ="dropdown" aria-expanded ="false" > 个人中心 </a > <ul class ="dropdown-menu" aria-labelledby ="navbarDropdown" > <li > <router-link class ="dropdown-item" :to ="{ name: 'user_bot_index' }" > 我的Bot</router-link > </li > <li > <hr class ="dropdown-divider" /> </li > <li > <a class ="dropdown-item" href ="#" > 退出</a > </li > </ul > </li > </ul > </div > </div > </nav > </template > <script > import { useRoute } from "vue-router" ;import { computed } from "vue" ;export default { setup ( const route = useRoute (); let route_name = computed (() => route.name ); return { route_name, }; }, }; </script > <style scoped > </style >
导入NavBar 现在还只是在src\components创建的一个公共组件,想要在页面中展示,必须在src\App.vue中引入
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 <template > <NavBar /> <router-view > </router-view > </template > <script > import NavBar from './components/NavBar.vue' import "bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" import "bootstrap/dist/js/bootstrap" export default { components :{ NavBar } } </script > <style > body { background-image : url ("./assets/images/background.jpg" ); background-size : cover; } </style >
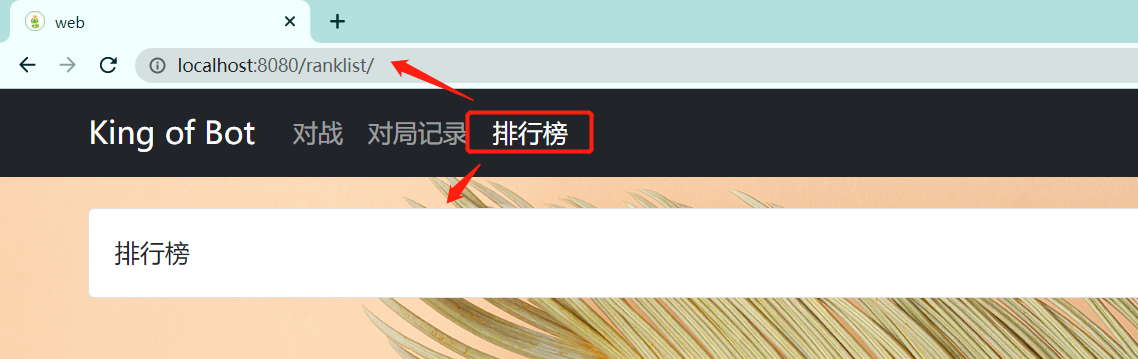
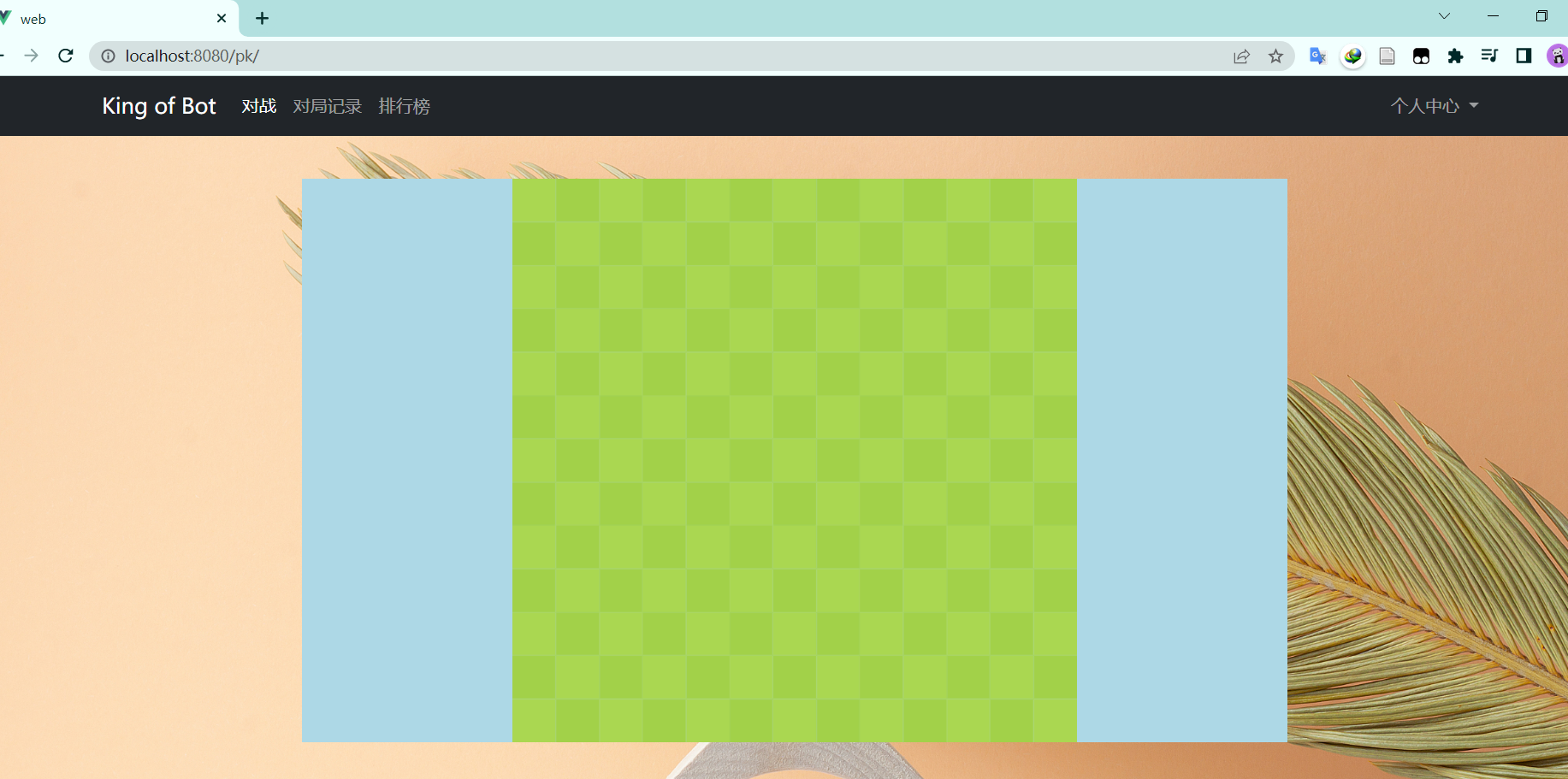
效果如下:
路由配置 如果将输入的网页,与对应的页面相一一对应,需要在src\router\index.js中配置路由
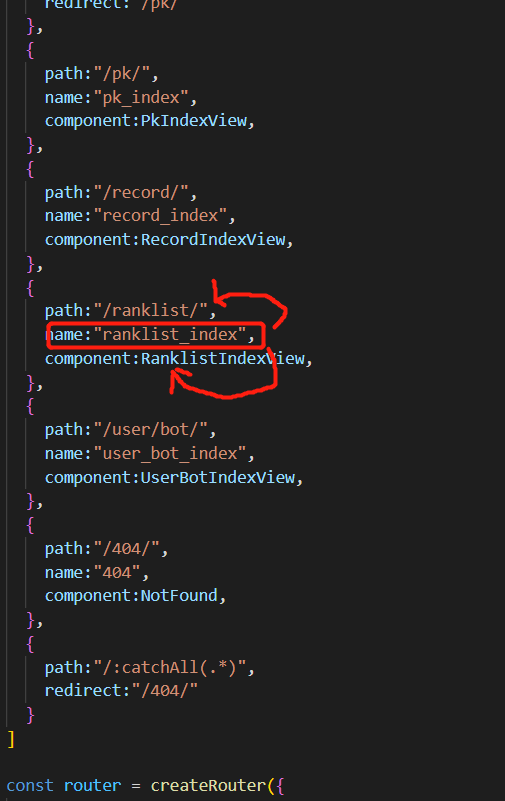
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router' import PkIndexView from "../views/pk/PkIndexView" import RecordIndexView from "../views/record/RecordIndexView" import RanklistIndexView from "../views/ranklist/RanklistIndexView" import UserBotIndexView from "../views/user/bot/UserBotIndexView" import NotFound from "../views/error/NotFound" const routes = [ { path :"/" , name :"home" , redirect :"/pk/" }, { path :"/pk/" , name :"pk_index" , component :PkIndexView , }, { path :"/record/" , name :"record_index" , component :RecordIndexView , }, { path :"/ranklist/" , name :"ranklist_index" , component :RanklistIndexView , }, { path :"/user/bot/" , name :"user_bot_index" , component :UserBotIndexView , }, { path :"/404/" , name :"404" , component :NotFound , }, { path :"/:catchAll(.*)" , redirect :"/404/" } ] const router = createRouter ({ history : createWebHistory (), routes }) export default router
其中的path就是浏览器的url,其中的component就是需要设置src\views下实现的基本页面。
src\views\pk\PkIndexView.vue代表对战页面
src\views\ranklist\RanklistIndexView.vue代表排行榜页面
src\views\record\RecordIndexView.vue代表对局记录页面
src\views\user\bot\UserBotIndexView.vue代表我的Bot页面
src\views\error\NotFound.vue代表404页面
这样就能实现输入url就能展示对应的页面
那如何实现点击页面的按钮元素,也能实现跳转页面呢,例如点击对局记录,也能跳转到当前页面
将按钮关联到路由名称
例如,点击排行榜
游戏页面 地图与障碍物 首先实现地图功能
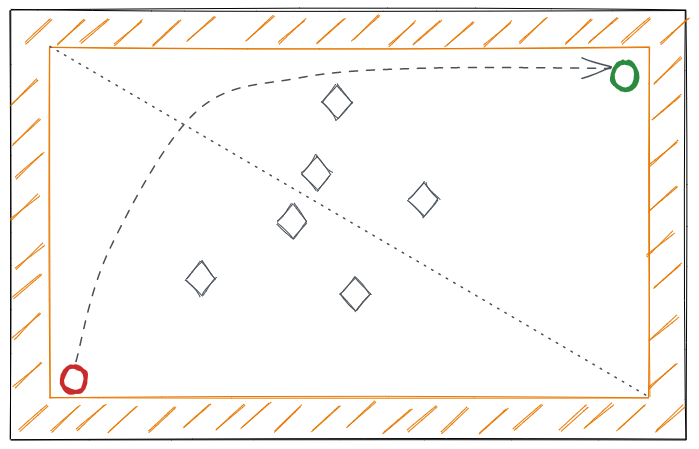
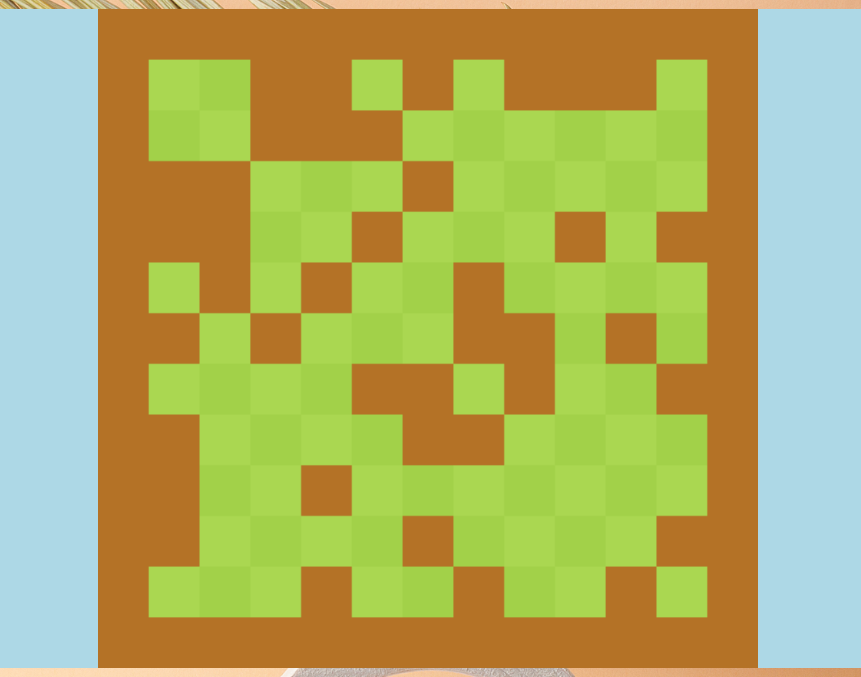
生成一个合法地图:
有边界
有随机、对称出现的障碍物
中心对称
初始时 两个Game Object分别在左下角和右上角
左下角和右上角是连通的(障碍物的布置有一定限制)
游戏中的每一个组件都是一个类,本次我们需要实现两个类,地图类和樯类,分别对应绿色部分和棕色部分。
对于所有类,我们还要实现一个基类。
基类GameObject 屏幕每秒钟刷新60次(也可以调整次数) 每次渲染出的画面称为帧 也就是一秒钟有60帧画面
那如何实现让物体的移动呢 需要依次计算出物体在每一帧下的位置 (每到下一帧 就要把上一帧画面全部覆盖重新画)最后渲染出的整体画面有产生了运动的效果。
在实现的过程中,关于运动这一点,需要抽象出一个基本的工具类,实现公共功能(凡是需要动的Object,每秒钟都要刷新60次即重画60次,都需要用到这样一个功能)
所有的Object都会用到这样一个工具类,我们就将其作为基类。
通常,工具类都放在src\assets\scripts中,用于存放常用脚本
创建GameObject.js
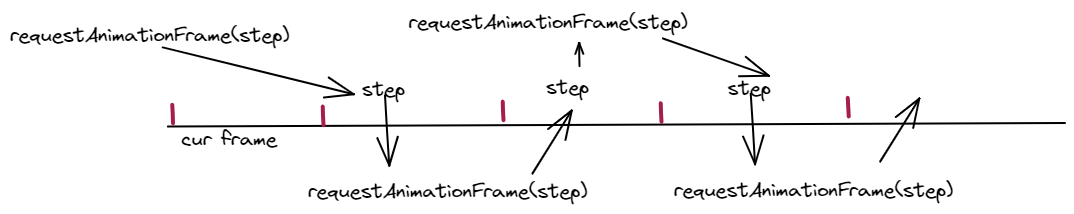
如何实现每秒钟所有的游戏对象都被刷新60次(一般浏览器的默认设置),借助requestAnimationFrame函数,传入一个回调函数step,那么这个回调函数就会在下一帧之内,也就是下一帧浏览器渲染之前执行一遍。
如何让step函数每一帧都执行,将其写成递归形式。
1 2 3 4 const step = ( requestAnimationFrame (step) } requestAnimationFrame (step)
这样,当我们开始调用requestAnimationFrame(step),会在下一帧执行step,在下一帧执行step时,执行完到最后再次触发requestAnimationFrame(step),会在下下帧执行step
就像下面这样,最终的结果就是每一帧都执行一次该step函数
此外,我们需要实现三个函数,分别是start,update,destroy
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 start ( } upadate (} on_destroy (} destroy ( this .on_destroy (); for (let i in GAME_OBJECTS ){ const obj = GAME_OBJECTS [i]; if (obj == this ){ GAME_OBJECTS .splice (i); break ; } } }
最终的结果是,所有GameObject对象的start函数在第一帧执行了一次(假设step函数开始执行的那一帧称为第一帧),后面的每一帧都执行upadate函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 const GAME_OBJECTS = [];export class GameObject { constructor ( GAME_OBJECTS .push (this ); this .timedelta = 0 ; this .has_called_start = false ; } start ( } upadate ( } on_destroy ( } destroy ( this .on_destroy (); for (let i in GAME_OBJECTS ){ const obj = GAME_OBJECTS [i]; if (obj == this ){ GAME_OBJECTS .splice (i); break ; } } } } let last_timestemp;const step = timestemp =>{ for (let obj of GameObjects ){ if (!obj.has_called_start ){ obj.has_called_start = true ; obj.start (); }else { obj.timedelta = timestemp - last_timestemp; obj.upadate (); } } last_timestemp = timestemp; requestAnimationFrame (step) } requestAnimationFrame (step)
地图类GameMap 用于实现地图
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/
需要用到Canvas API
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Canvas_API
障碍物类Wall 在src\assets\scripts\Wall.js中定义障碍物类Wall
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 import { GameObject } from "./GameObject" ;export class Wall extends GameObject { constructor (r, c, gamemap ){ super (); this .r = r; this .c = c; this .gamemap = gamemap; this .color = "#b47226" ; } update ( this .render (); } render ( const L = this .gamemap .L ; const ctx = this .gamemap .ctx ; ctx.fillStyle = this .color ; ctx.fillRect (this .c * L, this .r * L, L, L); } }
在src\assets\scripts\GameMap.js中创建,例如new Wall(0,0,this)表示在(0,0)这个格子处渲染出一个障碍物来
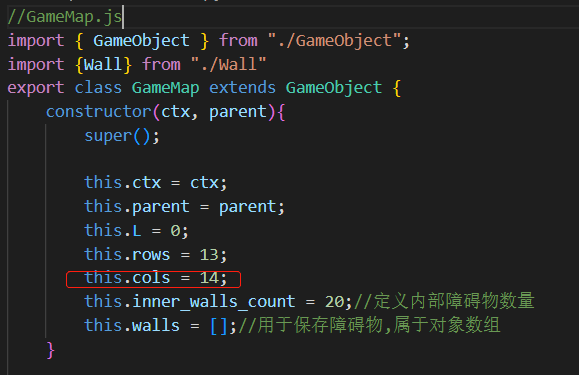
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 import { GameObject } from "./GameObject" ;import {Wall } from "./Wall" export class GameMap extends GameObject { constructor (ctx, parent ){ super (); this .ctx = ctx; this .parent = parent; this .L = 0 ; this .rows = 13 ; this .cols = 13 ; this .walls = []; } create_walls ( new Wall (0 ,0 ,this ); } start ( this .create_walls (); } ...
如果改为给两侧全部加上障碍物,则create_walls()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 create_walls ( const g = []; for (let r = 0 ; r < this .rows ; r++){ g[r] = []; for (let c = 0 ; c < this .cols ; c++){ g[r][c] = false ; } } for (let r = 0 ; r < this .rows ; r++){ g[r][0 ]=true ; g[r][this .cols -1 ]=true ; } for (let c = 0 ; c < this .cols ; c++){ g[0 ][c] = g[this .rows -1 ][c] = true ; } console .log (g); for (let r = 0 ; r < this .rows ; r++){ for (let c = 0 ; c < this .cols ; c++){ if (g[r][c]){ this .walls .push (new Wall (r,c,this )); } } } }
为什么障碍物的颜色会覆盖地图的颜色呢?是因为后创建的对象会将前面的对象覆盖掉。
在内部设置障碍物:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 for (let i = 0 ; i < this .inner_walls_count / 2 ; i++){ for (let j = 0 ; j < 1000 ; j++) { let r = parseInt (Math .random ()*this .rows ); let c = parseInt (Math .random ()*this .cols ); if (g[r][c] || g[c][r]) continue ; if (r == this .rows - 2 && c == 1 || r == 1 && c == this .cols -2 ) continue ; g[r][c] = g[c][r] = true ; break ; } }
如何保证连通性呢,也就是如何让找到一条从左下角到右上角的,没有障碍物的路。
通过加入一个check_connectivity函数,来判断当前地图状态是否具有连通性
最终代码:
src\assets\scripts\GameMap.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 import { GameObject } from "./GameObject" ;import {Wall } from "./Wall" export class GameMap extends GameObject { constructor (ctx, parent ){ super (); this .ctx = ctx; this .parent = parent; this .L = 0 ; this .rows = 13 ; this .cols = 13 ; this .inner_walls_count = 20 ; this .walls = []; } check_connectivity (g, sx, sy, tx, ty ){ if (sx == tx && sy == ty) return true ; g[sx][sy] = true ; let dx = [-1 , 0 , 1 , 0 ]; let dy = [0 , 1 , 0 , -1 ]; for (let i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++){ let x = sx + dx[i]; let y = sy + dy[i]; if (!g[x][y] && this .check_connectivity (g, x, y, tx, ty)) return true ; } return false ; } create_walls ( const g = []; for (let r = 0 ; r < this .rows ; r++){ g[r] = []; for (let c = 0 ; c < this .cols ; c++){ g[r][c] = false ; } } for (let r = 0 ; r < this .rows ; r++){ g[r][0 ]=true ; g[r][this .cols -1 ]=true ; } for (let c = 0 ; c < this .cols ; c++){ g[0 ][c] = g[this .rows -1 ][c] = true ; } for (let i = 0 ; i < this .inner_walls_count / 2 ; i++){ for (let j = 0 ; j < 1000 ; j++) { let r = parseInt (Math .random ()*this .rows ); let c = parseInt (Math .random ()*this .cols ); if (g[r][c] || g[c][r]) continue ; if (r == this .rows - 2 && c == 1 || r == 1 && c == this .cols -2 ) continue ; g[r][c] = g[c][r] = true ; break ; } } const copy_g = JSON .parse (JSON .stringify (g)); if (!this .check_connectivity (copy_g,this .rows -2 ,1 ,1 ,this .cols -2 )) return false ; for (let r = 0 ; r < this .rows ; r++){ for (let c = 0 ; c < this .cols ; c++){ if (g[r][c]){ this .walls .push (new Wall (r,c,this )); } } } return true ; } start ( for (let i = 0 ; i < 1000 ; i++) { if (this .create_walls ()) break ; } } update_size ( this .L = parseInt (Math .min (this .parent .clientWidth / this .cols , this .parent .clientHeight / this .rows )); this .ctx .canvas .width = this .L * this .cols ; this .ctx .canvas .height = this .L * this .rows ; } update ( this .update_size (); this .render (); } render ( const color_even = '#AAD751' const color_odd = '#A2D149' for (let r = 0 ; r < this .rows ; r++){ for (let c = 0 ; c < this .cols ; c++){ if (( r + c ) % 2 == 0 ){ this .ctx .fillStyle = color_even; }else { this .ctx .fillStyle = color_odd; } this .ctx .fillRect (c* this .L , r* this .L , this .L , this .L ); } } } }
蛇的运动 先来解决之前存在的一个问题,在13*13的地图环境下:
两条蛇的初始坐标为(11,1)和(1,11)
(11,1)起点,横纵坐标相加为偶数,随着运动,奇数,偶数,…
(1,11)起点,横纵坐标相加为偶数,随着运动,奇数,偶数,…
由于同一时刻,奇偶性相同,因此,有可能走到同一个格子中。
修改,对应的起点(11,1)和(1,12)所以两条蛇一定不会走到同一个格子里。
相应的,对称的布局应该为中心对称
创建单元类Cell 在构造器中,传入行(r)和列(c)信息,并将其转换为坐标信息
src\assets\scripts\Cell.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 export class Cell { constructor (r,c ){ this .r = r; this .c = c; this .x = c + 0.5 ; this .y = r + 0.5 ; } }
创建蛇类Snack src\assets\scripts\Snack.js
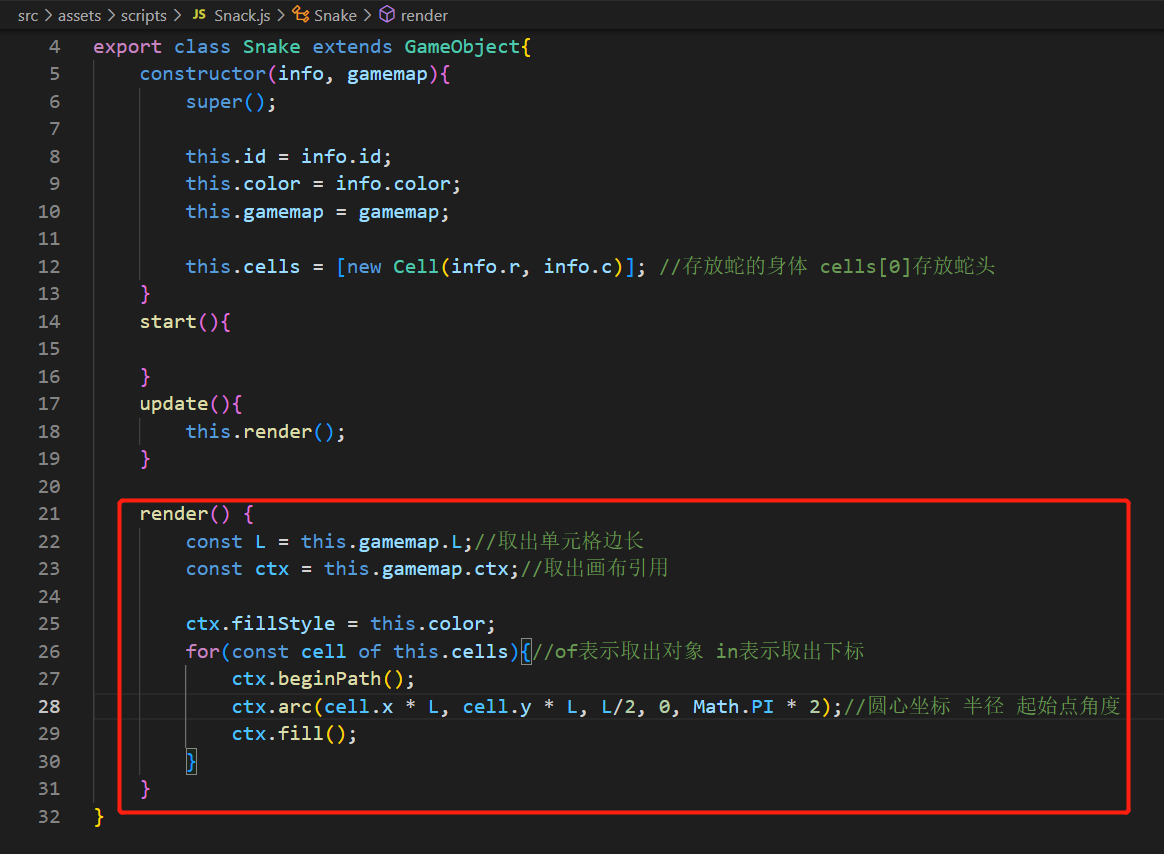
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 import { GameObject } from "./GameObject" ;import { Cell } from "./Cell" ;export class Snake extends GameObject { constructor (info, gamemap ){ super (); this .id = info.id ; this .color = info.color ; this .gamemap = gamemap; this .cells = [new Cell (info.r , info.c )]; } start ( } update ( this .render (); } render ( } }
实例化蛇类 在src\assets\scripts\GameMap.js中,将两条蛇创建出来(也就是实例化两个Snack类的对象)
将蛇画出来 src\assets\scripts\Snack.js
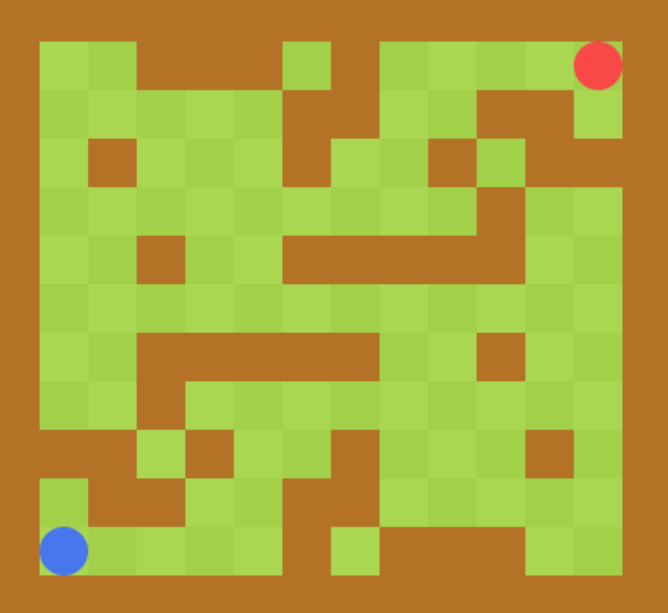
效果如下:
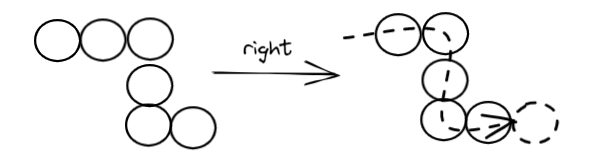
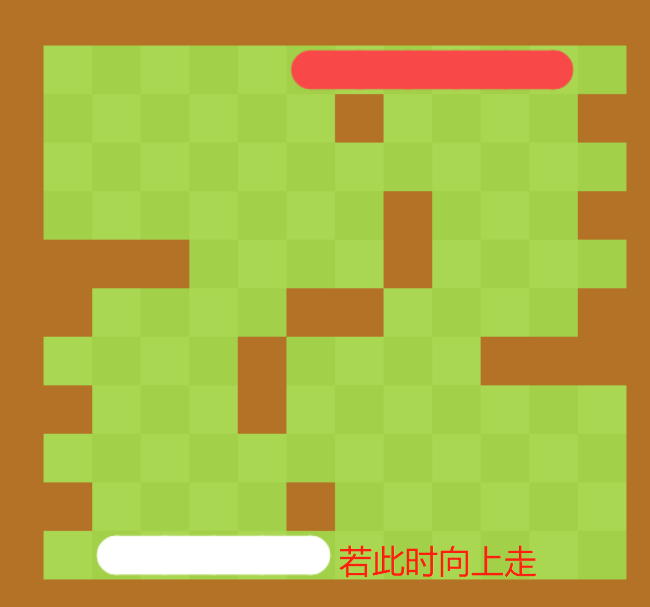
蛇的运动 怎么动 1)如果只有一个单元
定义一个速度变量speed,并且在每一帧的刷新函数中,计算蛇的坐标
2)如果多个单元
例如下面的场景向右移动一格
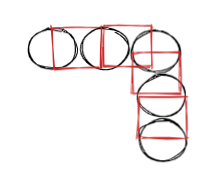
但魔鬼都在细节之中,正常移动的过程会产生不连贯的现象
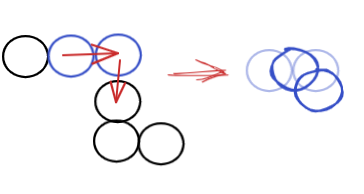
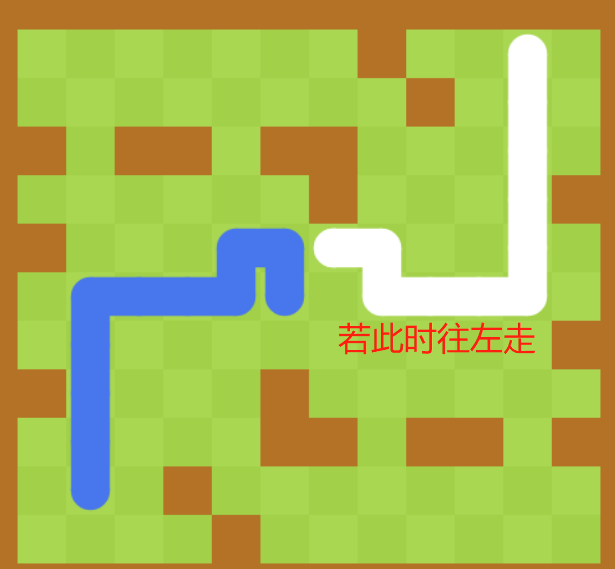
那如何更好的移动的呢:
创建一个虚拟头结点,只让虚拟头结点和尾结点移动,其余结点保持不变。这样在拐角处一直保持连贯性。
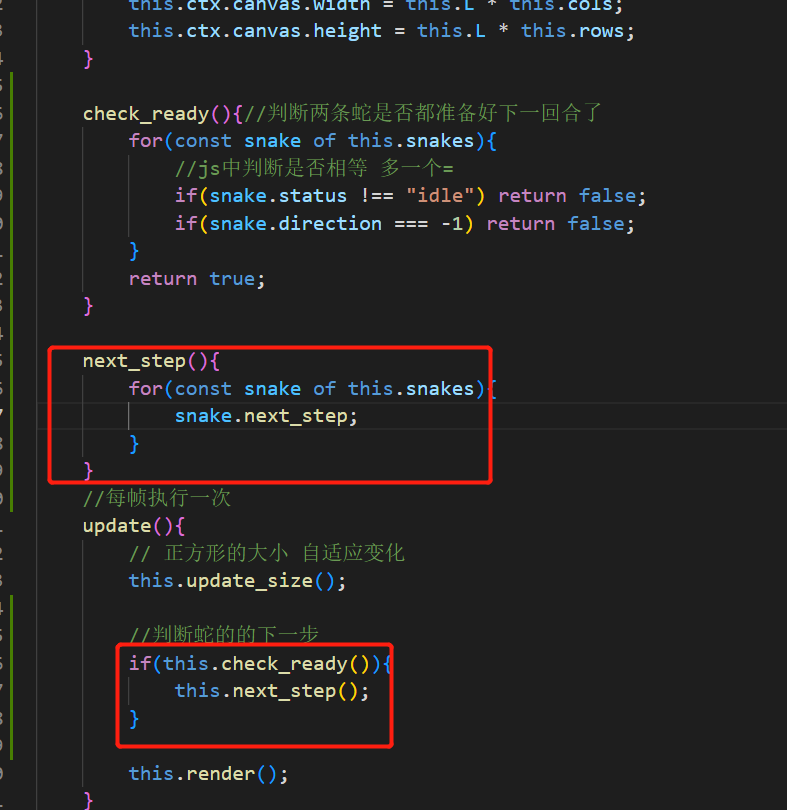
什么时候动 由于我们设计的是回合制游戏,所以需要当判断出两条蛇都有下一步指令的时候,才应该按照指令,分别动一步。
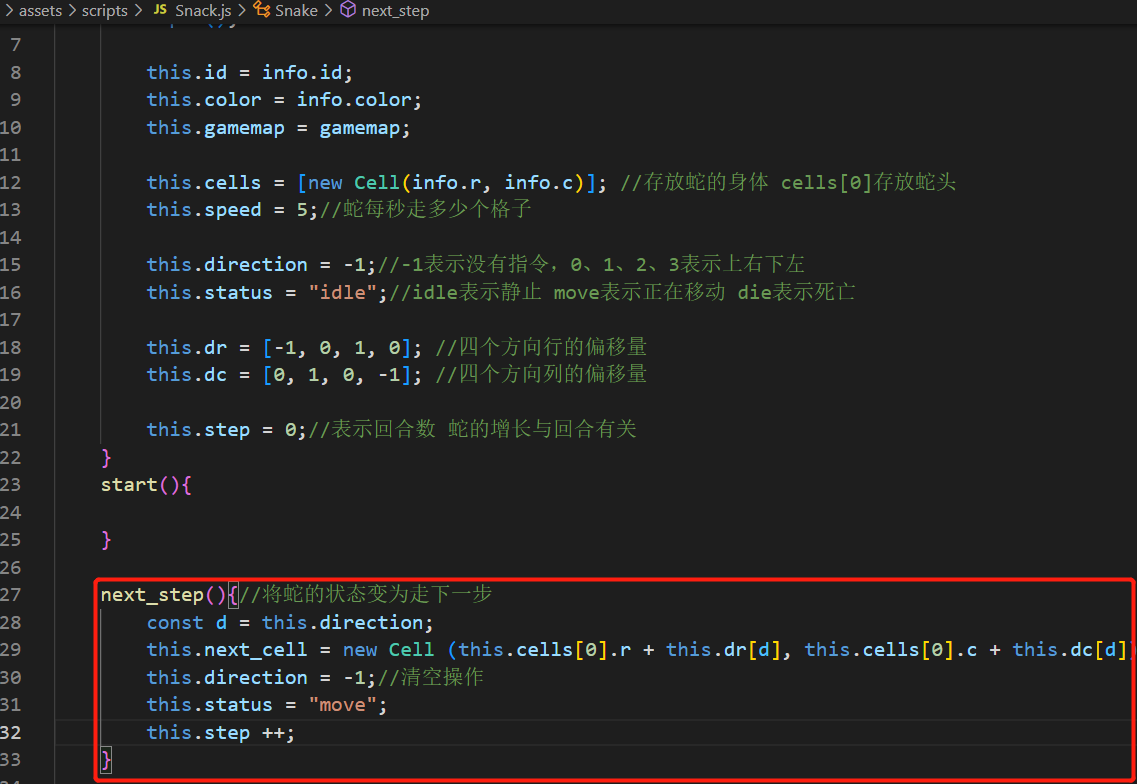
首先在src\assets\scripts\Snack.js记录当前蛇收到的指令,以及蛇的状态
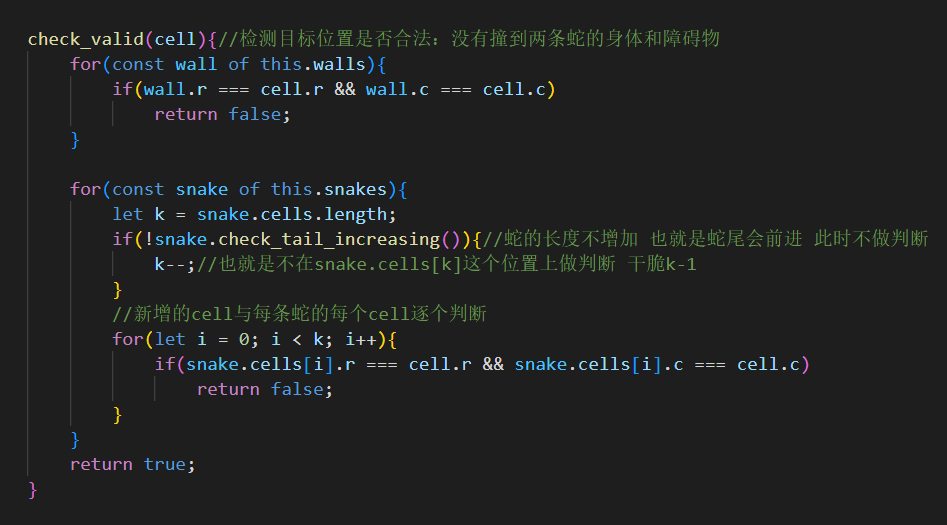
其次,还要有裁判来判断蛇是否能动(不能由蛇自己判断 运动员本身不能当裁判)
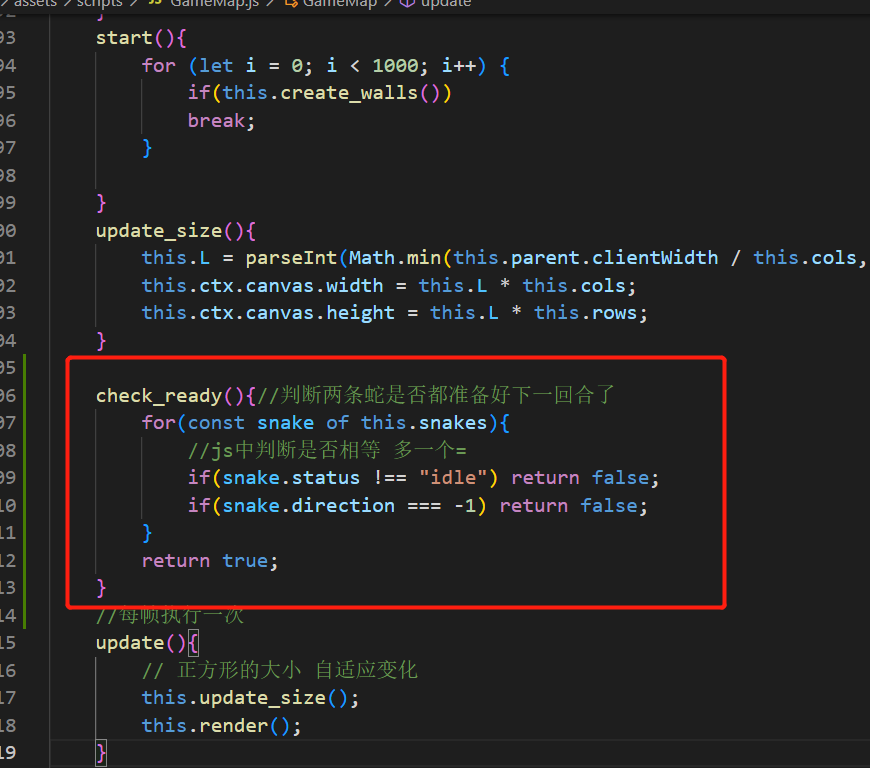
我们将裁判的逻辑放在src\assets\scripts\GameMap.js中
如果准备好了下一回合,就让蛇走下一步:
src\assets\scripts\Snack.js中,蛇走下一步函数的定义如下:
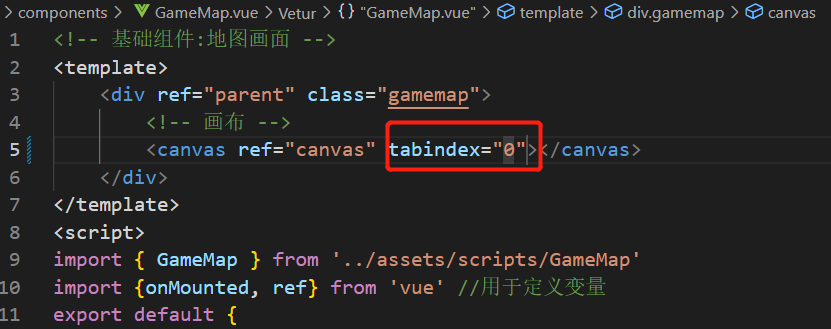
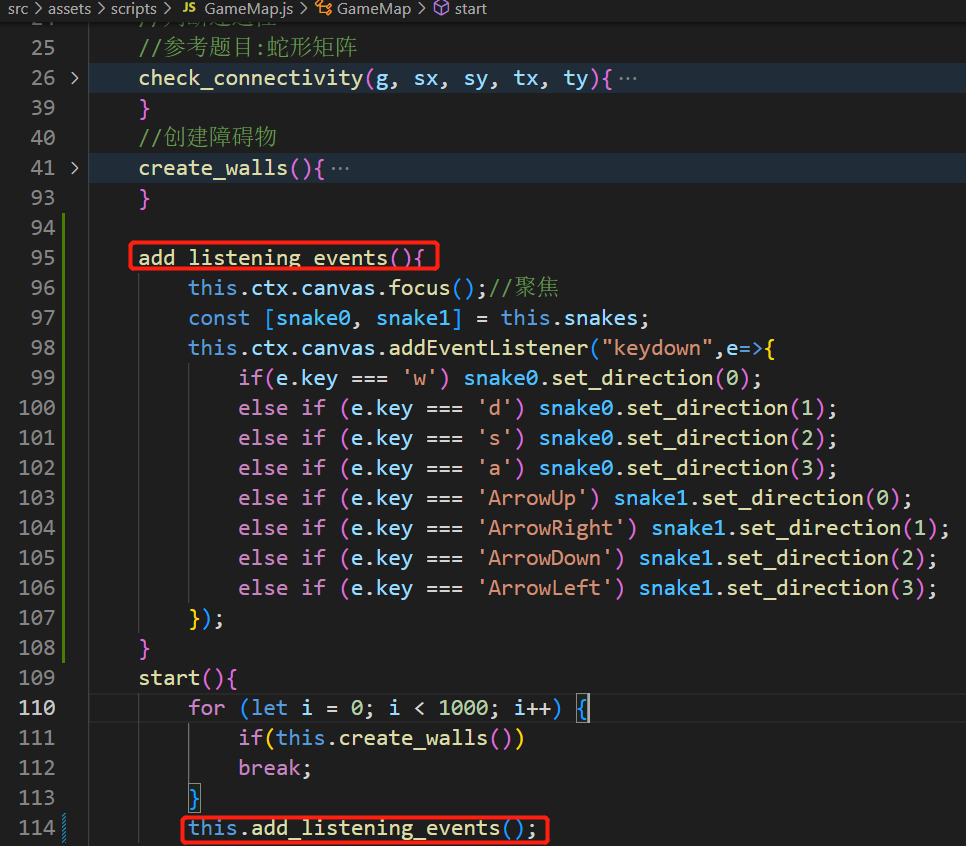
获取用户操作 在src\components\GameMap.vue中给canvas新增属性tabindex="0",可以获取用户操作
在src\assets\scripts\GameMap.js中为canvas绑定一个获取用户输入信息的事件
控制蛇的移动 对于蛇的移动来说
先考虑除了头元素之外的其他元素
蛇的前进是新增头元素(有时砍掉尾元素的过程 后面会讲到)
而新增头元素,剩余其他的下标顺序都要往后移动
在src\assets\scripts\Snack.js中
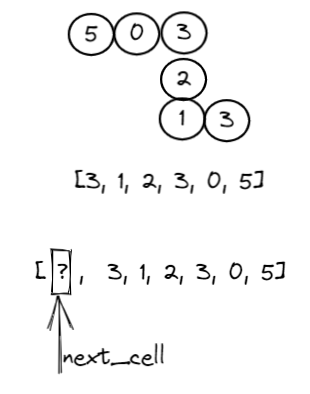
此时cell[0]的位置就腾出来了,然后需要将cell[0]指向next_vell的位置
先看下如何移动蛇头元素:
蛇头移动 需要根据与目标元素(也就是next_cell)的的位置和蛇头当前的位置(this.cells[0])来决定this.cells[0]的x和y坐标接下来的变化。
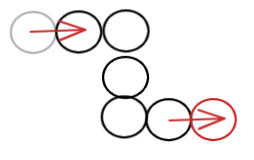
此时已经可以达到移动效果:
此时实现了蛇头的移动,但是还没有实现蛇尾移动。
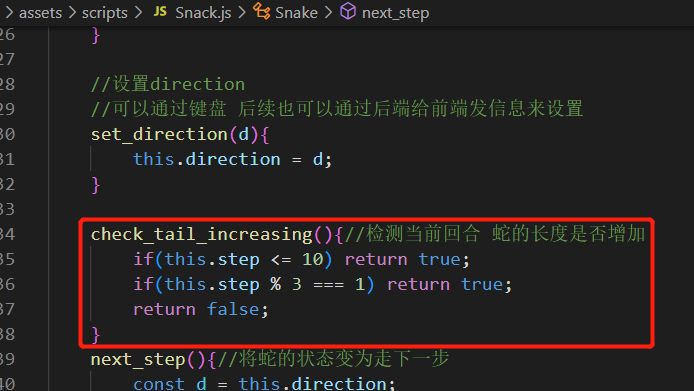
蛇尾移动 首先在src\assets\scripts\Snack.js增加判断蛇的长度是否增加的函数
我们规定,前10回合,蛇的长度每回合+1,后面的回合,每3回合+1,也就是第13,16,19…
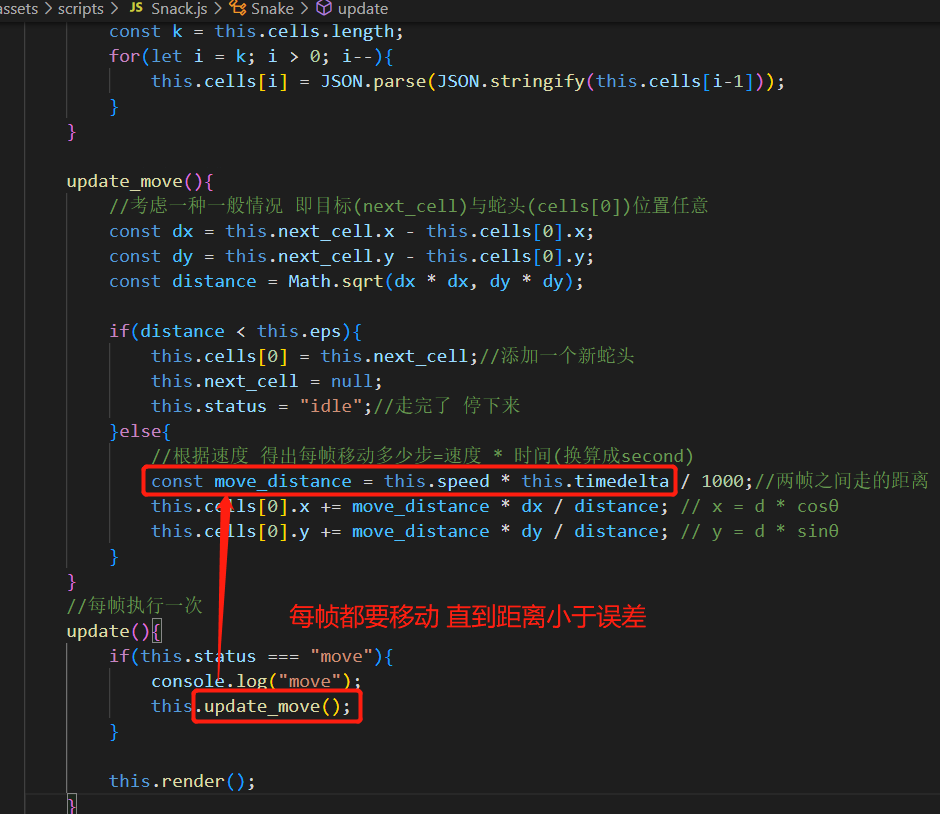
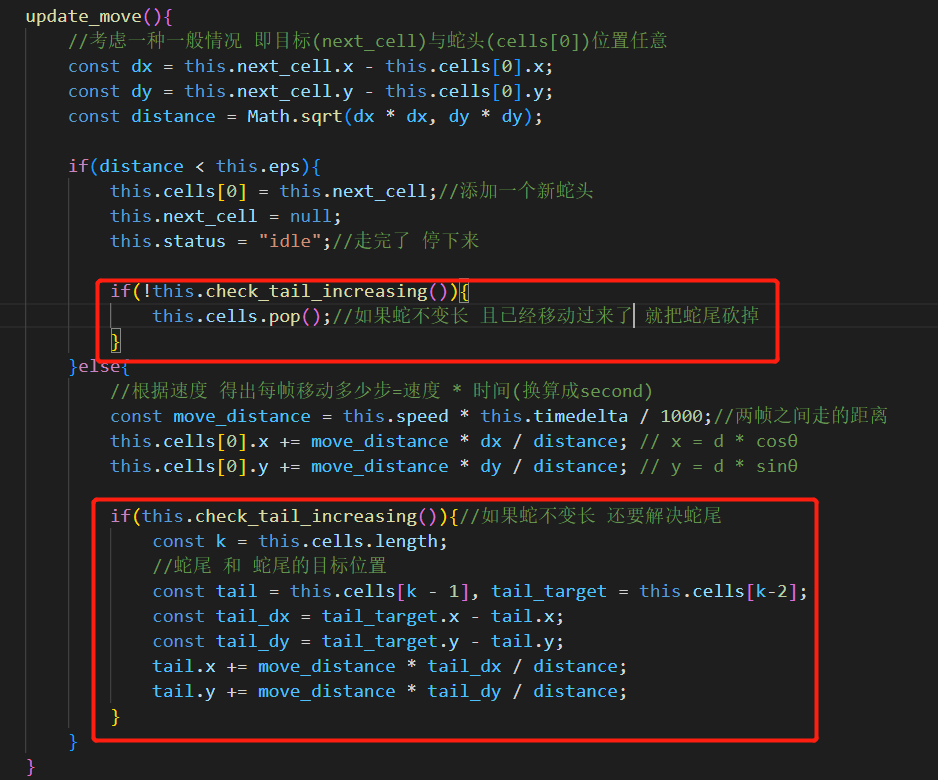
如果需要变长,那么蛇尾不动即可;如果不变长,那么蛇尾就要跟着蛇头移动(并且移动完,要将蛇尾砍掉,从对象数组中移走)于是在update_move()中更新如下
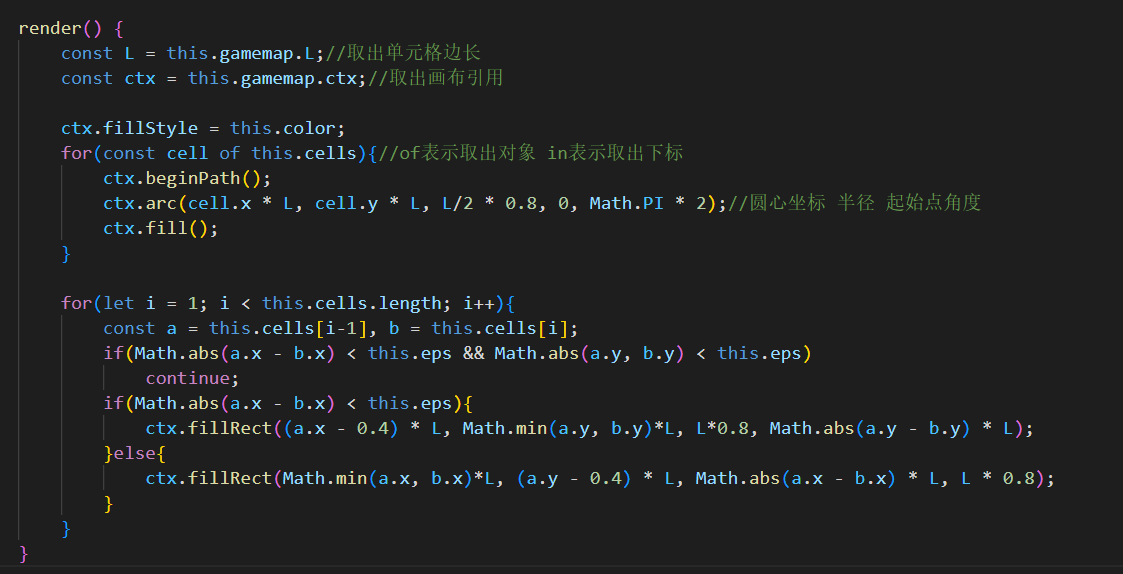
美化 1)让蛇形体更连贯
2)让蛇更瘦
更新render()
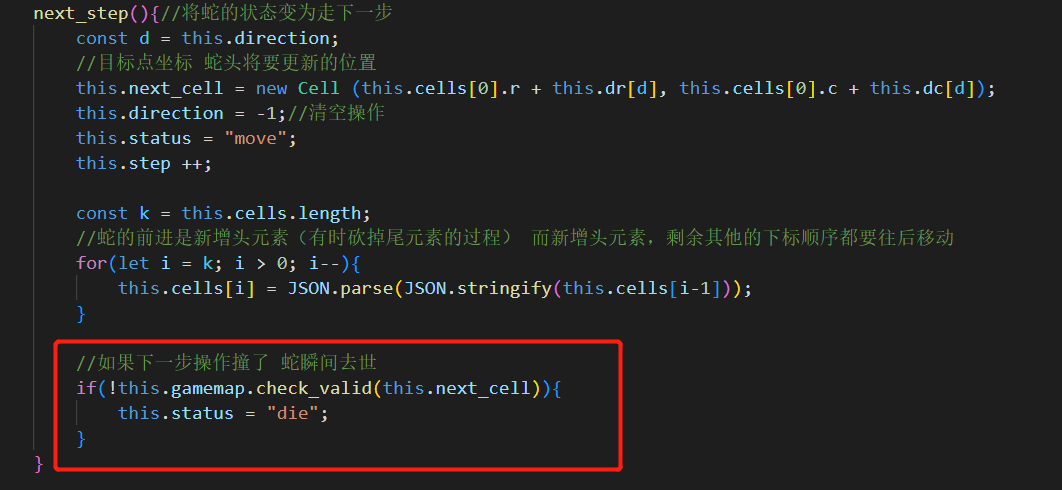
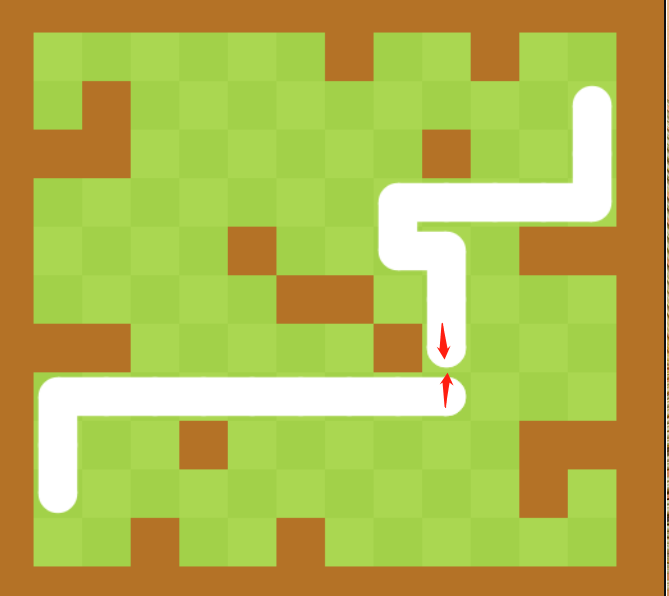
合法性判断 我们还要在src\assets\scripts\GameMap.js中加入合法性判断,用于检测目标位置是否合法
在src\assets\scripts\Snack.js中的next_step(),要针对这种判断做出反应
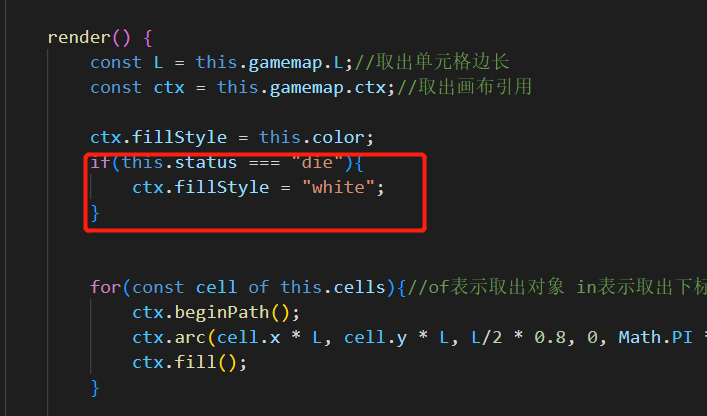
并在render()中加入绘图逻辑,当蛇over的时候,颜色变白
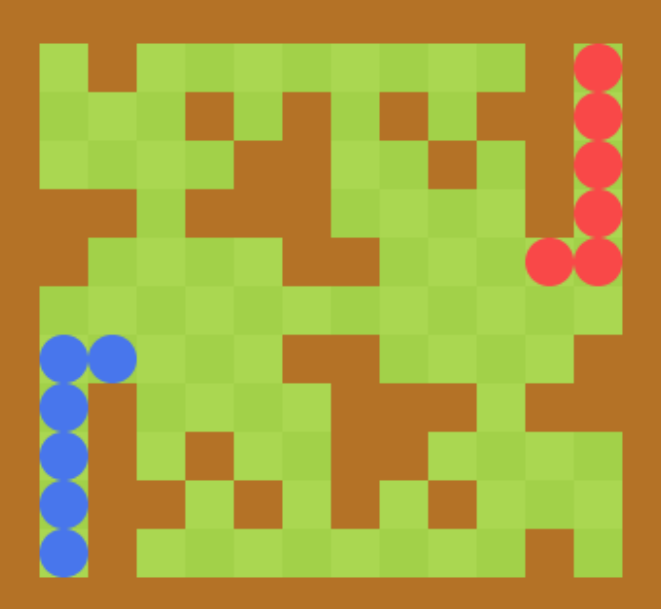
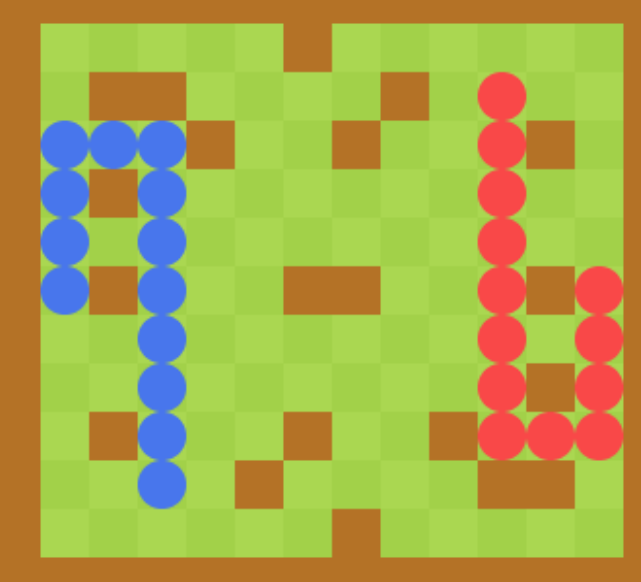
结果展示:
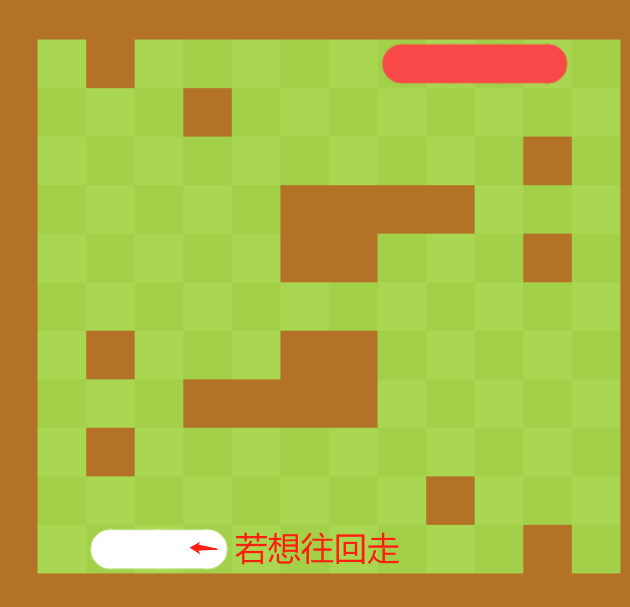
往回走也是不行,因为相当于自己和之前的cell装机
注意,两条蛇的合法性判断是独立的。当两条蛇的蛇头位置都不合法时,平局
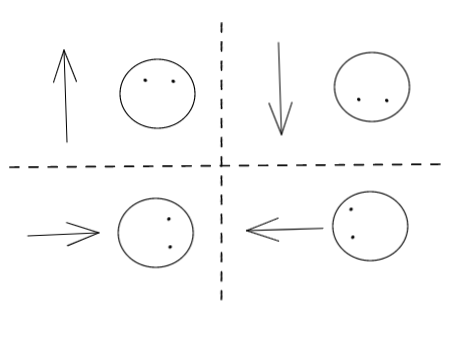
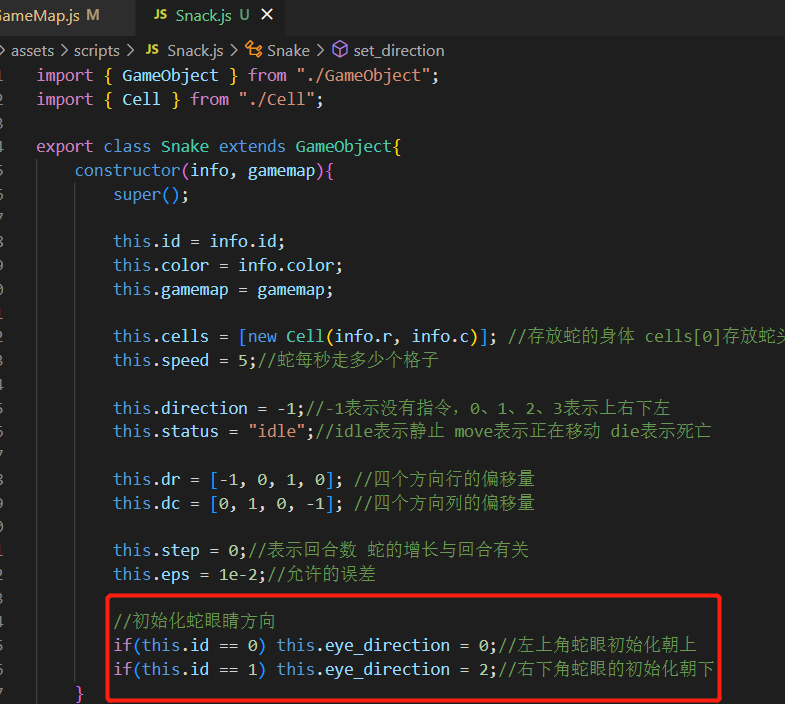
蛇的美化 为蛇头添加眼睛
初始化Snack类时候,初始化一个eye_direction变量表示蛇的眼睛方向
然后在每次执行next_step()函数时,更新eye_direction变量
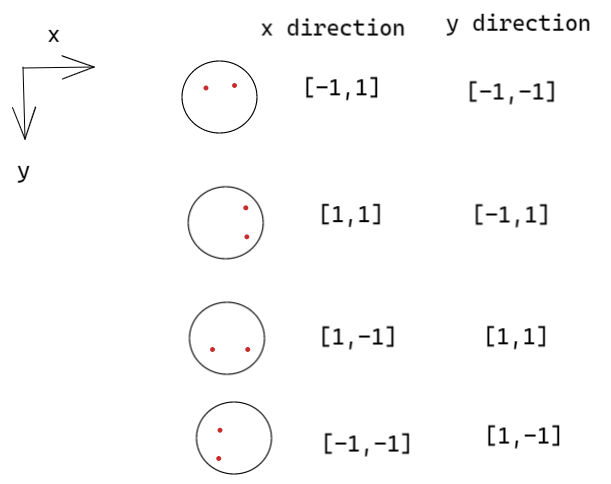
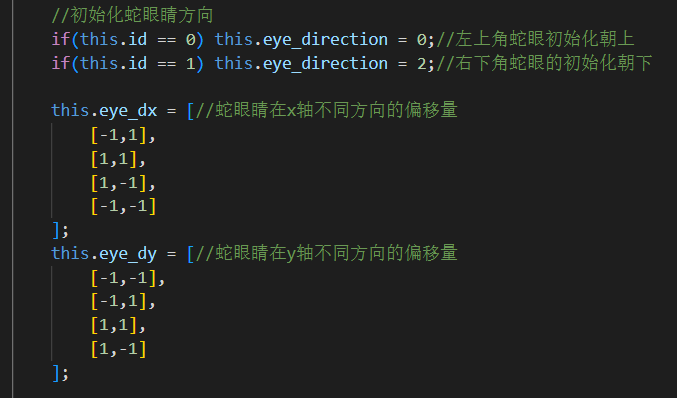
计算蛇眼睛在不同方向上的偏移量
最后在render()函数中画蛇眼睛
然后保存代码:
查看历史记录