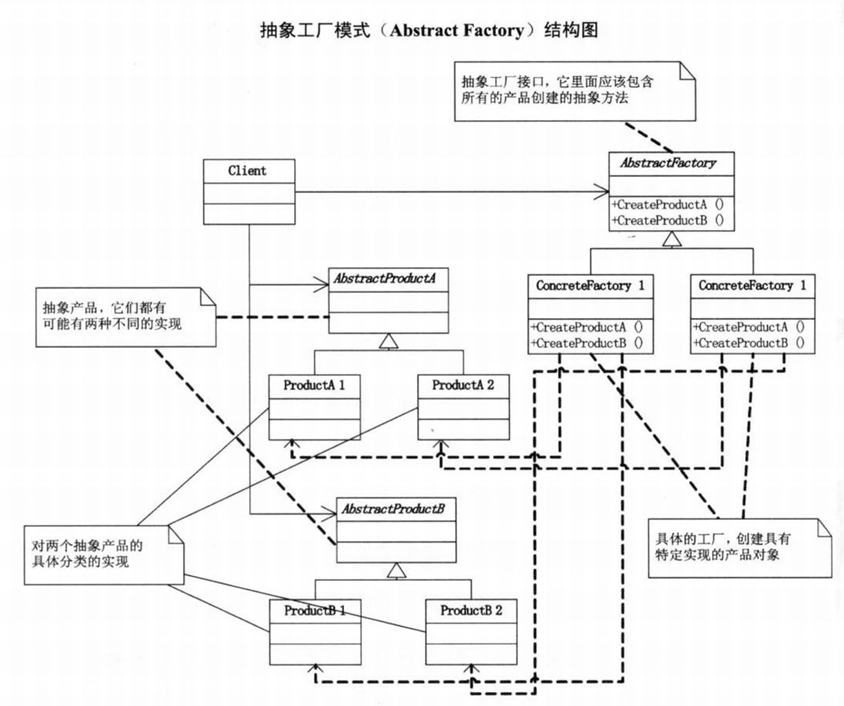
抽象工厂模式
抽象工厂模式是工厂方法模式的泛化版,工厂方法模式是一种特殊的抽象工厂模式。在抽象工厂模式中,每一个具体工厂可以生产多个具体产品。
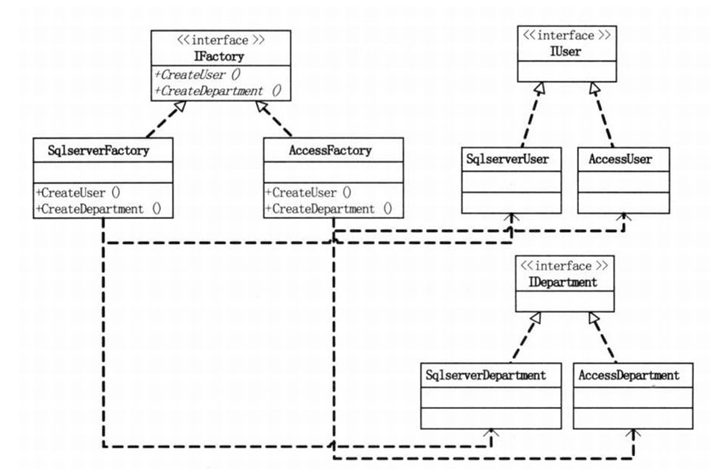
类图示例
举个例子
数据库工厂,由用户表和部门表,可以用SQLServer和Access数据库
代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
|
class User {
private String name;
private int id;
public int GetId() {
return id;
}
void SetId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
String GetName() {
return name;
}
void SetName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
class Department {
private String name;
private int id;
public int GetId() {
return id;
}
void SetId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
String GetName() {
return name;
}
void SetName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
interface IUser {
void Insert(User user);
User GetUser(int id);
}
class SqlServerUser implements IUser {
public void Insert(User user) {
System.out.println("在SQL server中给User表增加一条记录");
}
public User GetUser(int id) {
System.out.println("在SQL server中根据ID得到User表一条记录");
return null;
}
}
class AccessUser implements IUser {
public void Insert(User user) {
System.out.println("在Access中给User表增加一条记录");
}
public User GetUser(int id) {
System.out.println("在Access中根据ID得到User表一条记录");
return null;
}
}
interface IDepartment {
void Insert(Department department);
Department GetDepartment(int id);
}
class SqlServerDepartment implements IDepartment {
public void Insert(Department department) {
System.out.println("在SQL server中给Department表增加一条记录");
}
public Department GetDepartment(int id) {
System.out.println("在SQL server中根据ID得到Department表一条记录");
return null;
}
}
class AccessDepartment implements IDepartment {
public void Insert(Department department) {
System.out.println("在Access中给Department表增加一条记录");
}
public Department GetDepartment(int id) {
System.out.println("在Access中根据ID得到Department表一条记录");
return null;
}
}
interface IFactory {
IUser createUser();
IDepartment createDepartment();
}
class SqlServerFactory implements IFactory {
public IUser createUser() {
return new SqlServerUser();
}
public IDepartment createDepartment() {
return new SqlServerDepartment();
}
}
class AccessFactory implements IFactory {
public IUser createUser() {
return new AccessUser();
}
public IDepartment createDepartment() {
return new AccessDepartment();
}
}
public class AbstractFactory {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = new User();
Department department = new Department();
IFactory factory = new SqlServerFactory();
IUser iu = factory.createUser();
iu.Insert(user);
iu.GetUser(1);
IDepartment id = factory.createDepartment();
id.Insert(department);
id.GetDepartment(1);
}
}
|
该例子的类图示例
抽象工厂模式包含如下角色
- AbstractFactory(抽象工厂),抽象工厂用于声明生成抽象产品的方法,在一个抽象工厂中可以定义一组方法,每一个,方法对应一个产品等级结构。
- ConcreteFactory(具体工厂),具体工厂实现了抽象工厂声明的生成抽象产品的方法,生成一组具体产品,这些产品构,成了一个产品族,每一个产品都位于某个产品等级结构中。
- AbstractProduct(抽象产品),抽象产品为每种产品声明接口,在抽象产品中定义了产品的抽象业务方法。
- ConcreteProduct(具体产品),具体产品定义具体工厂生产的具体产品对象,实现抽象产品接口中定义的业务方法。
模式分析
好处是易于交换产品,由于具体工厂类在一个应用中只需要在初始化的时候出现一次,这就使得
改变一个应用的具体工厂变得非常容易,它只需要改变具体工厂即可使用不同的产品配置。另外,他让
具体的创建实例过程与客户端分离,客户端是通过他们的抽象接口操作实例,产品的具体类名也被具体
工厂的实现分离,不会出现在客户代码中




